CRISPR-PLANT
A Portal of CRISPR-Cas9 Mediated Genome Editing
Analysis strategy and bioinformatic pipeline
The gRNA-Cas9 recognizes targets based on gRNA-DNA pairing, the specificity of each gRNA spacer sequences could be predicted by genome-wide sequence comparison with other spacers. With available criteria regarding the gRNA-Cas9 specificity and off-target potential in animal and plant systems, we calculate specificity of all gRNA spacer sequences based on both mismatches number and position in their alignments with other spacer sequences. The choice of gRNA spacer sequences is limited to locations of PAMs in the genome. Cas9 recognizes two PAMs (5'-NGG-3' or 5'-NAG-3') but shows much less affinity to NAG-PAM sites. Thus, we only recommend gRNA spacer sequences to target NGG-PAM sites (GG-spacer). The spacer sequences targeting NAG-PAM sites (AG-spacer) were also extracted but only used for off-target assessment. We classified NGG-PAM spacer sequences into following categories according to their specificity.
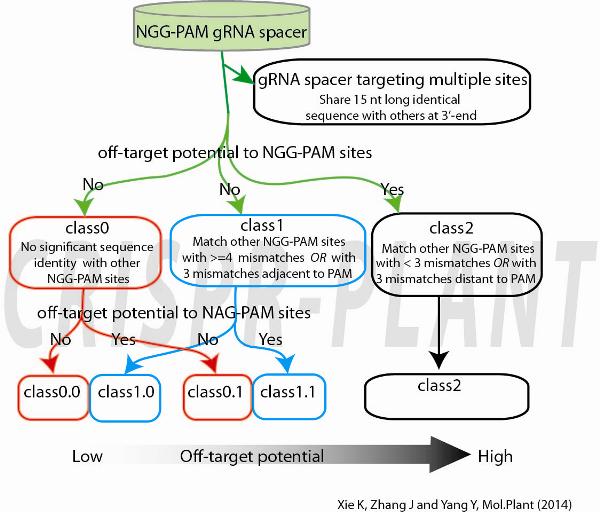
- Each spacer candidate was classified to Class0, 1 and 2 according to their off-target potential to other NGG-PAM sites.
- Class0: no significant sequence identity with other GG-spacer;
- Class1: four or more mismatches, or three mismatches adjacent to PAM in all alignments with GG-spacer;
- Class2: fewer than three mismatches, or three mismatches distant to PAM in all alignments with GG-spacer;
- Class0 and Class1 spacer sequences were further classified according their off-target potential to NAG-PAM sites.
- Class0.0 and Class1.0, match any AG-spacer with more than 2 mismatches;
- Class0.1 and Class1.1, match any AG-spacer with equal or fewer than 2 mismatches;
Class0.0 and class1.0 gRNA spacers are considered specific for CRISPR-Cas9 mediated genome editing.
We introduced minMM value to evaluate spacer sequence specificity for designing gRNAs. The minMM value is the minimal mismatch number in all alignments after genome-wide sequence paring. Please note that we considered both gap and substitution as mismatch in a sequence alignment for minMM calculation.
If you are interesting in details about our analysis pipeline, please contact us.How to use searching function
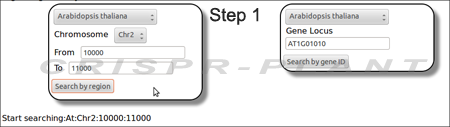
The CRISPR-PLANT data could be accessed by three simple steps
- Select plant specie and chromosome region or gene of interest to start searching gRNA spacer sequences.
- Searching gRNA spacers by inputting a chromosome region;
- Searching a transcript unit or gene by inputting locus ID.
- Check the search result to identify gRNA spacer sequences that could be used to target selected gene or intergeneric region;
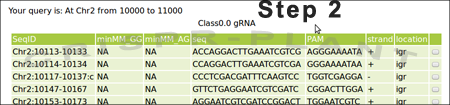
Currently, CRISPR-PLANT will show all Class0.0 and Class1.0 gRNA spacer sequences. We will add other gRNA spacer information in the near future. Following information will be listed for each spacer sequence:
- seqID: is shown as "Chromosome:start-end:strand". "strand" is show as empty for plus or "c" for minus, which indicates the chromosome strand of PAM. The start/end coordinates is zero indexed as BED format.
- minMM_GG: minMM (minimal mismatch number) value that was calculated from all alignments against other NGG-PAM spacer sequences. NA indicates no alignment was found.
- minMM_AG: minMM (minimal mismatch number) value that was calculated from all alignments against NAG-PAM spacer sequences.
- seq: sequence of gRNA spacer (20 nt long). For convenience, it is shown as DNA sequence (identical to protospacer).
- PAM: PAM with additional 7bp of genomic sequences.
- strand: chromosome strand of the PAM.
- location: intron/exon/igr(intergenic region) of gRNA targeted site. Location was based on one splice form even some genes have alternative splicing forms.
- last column:a click button to start analyzing spacer sequence.
- Browse and analyze searching results to find gRNA spacers which are best for your purpose.
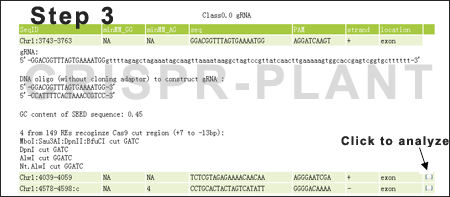
An analyzsis report will be shown after clicking the button in the last column. For restriction endonuclease (RE) cut analysis, click here to get the complete RE list used.
How to use Genome Browser
The out data could be accessed in the genome browser using JBrowse program with annotation and reference genomic sequence tracks. Additional annotation tracks could be loaded according to JBrowser instructions. Different classes of gRNA spacers are loaded as individual tracks in JBrowse. The names of gRNA spacer were coded as minMM_GG:minMM_AG. For example, a gRNA spacer named as 4:3 indicated minMM_GG=4 and minMM_AG=3. This setting may help you quickly locating best ones from dozens of spacers in an specific region. Please read instructions in JBrowser website for more information.
Data source
| Species | Group | GenBank Assembly ID | Release version | Genoem Annotation Source |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | dicot | GCA_000001735.1 | TAIR10 | TAIR |
| Medicago truncatula | dicot | GCA_000219495.1 | Mt3.5V4 | MIPS |
| Solanum lycopersicum | dicot | GCA_000188115.1 | SL2.40 | MIPS |
| Glycine max | dicot | GCA_000004515.1 | v1.1 | Phytozome |
| Brachypodium distachyon | monocot | GCA_000005505.1 | v1.2 | MIPS |
| Oryza sativa | monocot | GCA_000005425.2 | RGAP release 7 | RGAP |
| Sorghum bicolor | monocot | GCA_000003195.1 | Sorghum1.4 | MIPS |
| Zea mays | monocot | GCA_000005005.4 | B73 RefGen_v2: Release 5b.59 | maizeGDB |
CRISPR-PLANT is supported by Penn State and AGI.
CRISPR-PLANT©, 2014